Developer Guide
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Acknowledgements
- {list here sources of all reused/adapted ideas, code, documentation, and third-party libraries – include links to the original source as well}
- I, Bridget, used Claude Code to fix Checkstyle errors and improve code formatting across the codebase. All suggestions were reviewed before being applied.
- I, Jeffrey, used Claude to prettify the Release Notes into a markdown format.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
.puml files used to create diagrams are in this document docs/diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Architecture
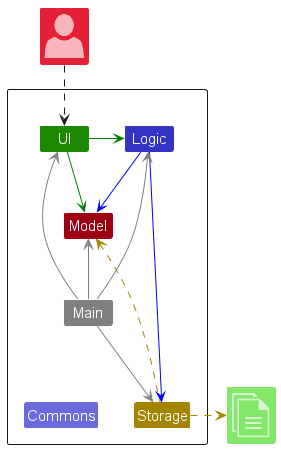
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app’s work is done by the following four components:
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
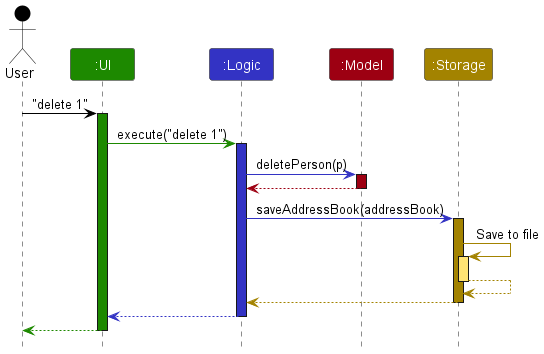
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
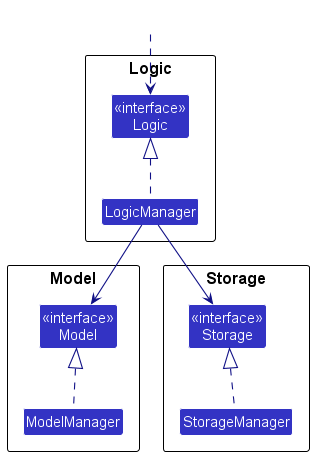
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component’s being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
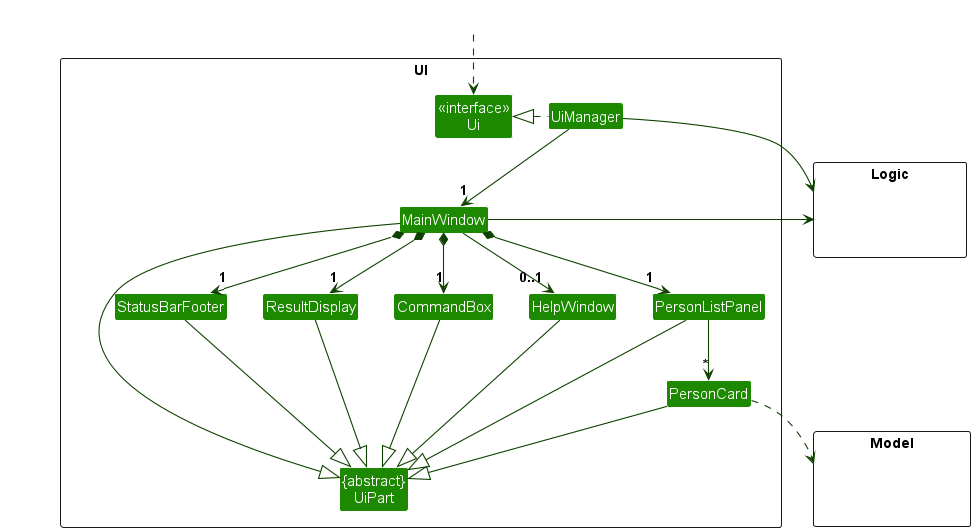
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, CompanyListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysCompanyobject residing in theModel.
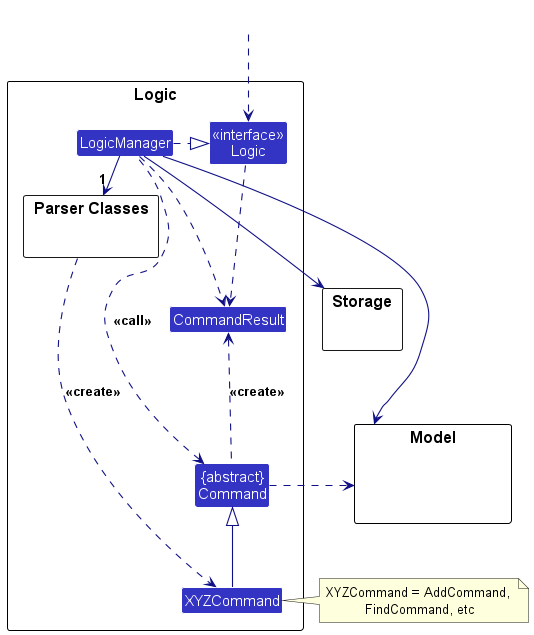
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here’s a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
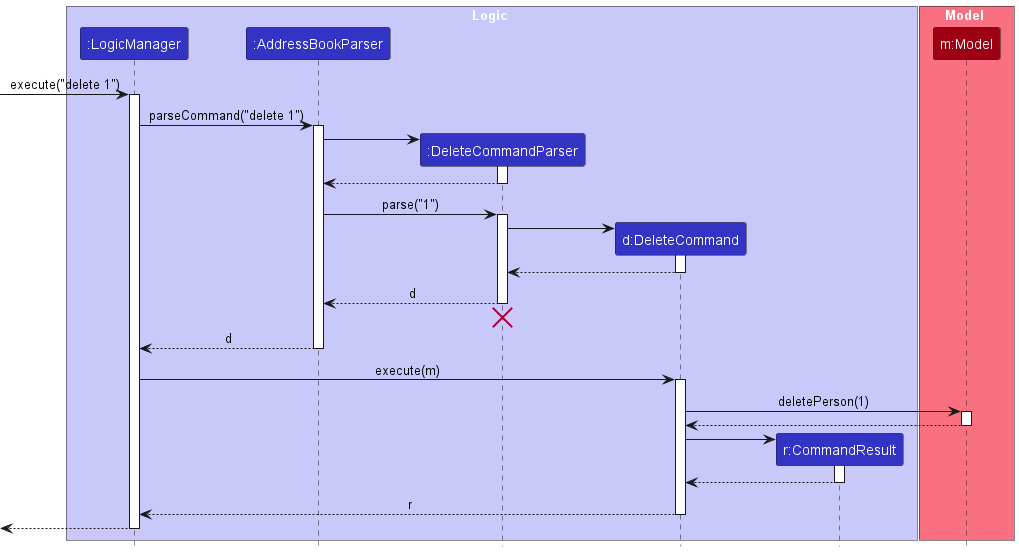
DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a company).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
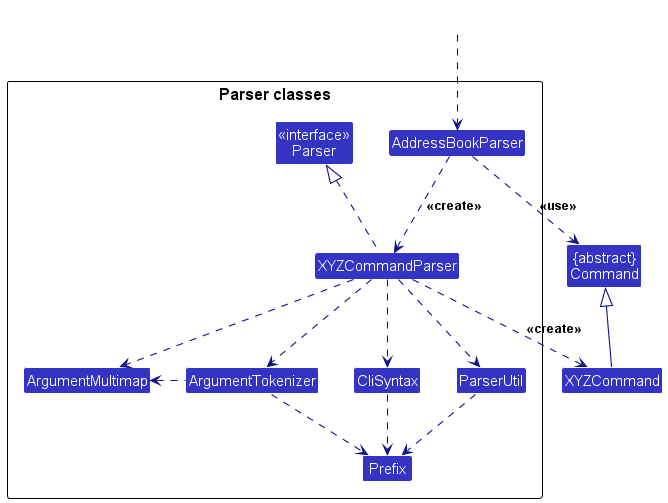
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, …) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
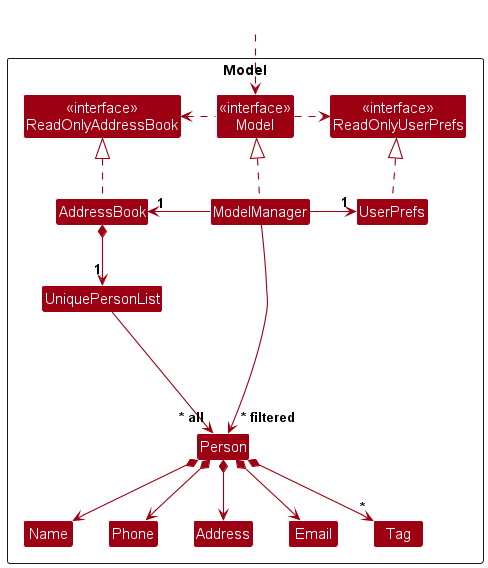
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Companyobjects (which are contained in aUniqueCompanyListobject). - stores the currently ‘selected’
Companyobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Company>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Tag list in the AddressBook, which Company references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Company needing their own Tag objects.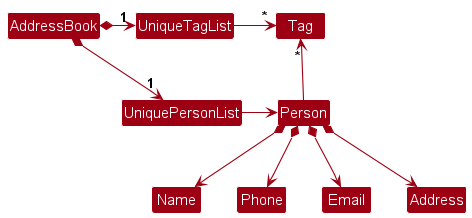
Storage component
API : Storage.java
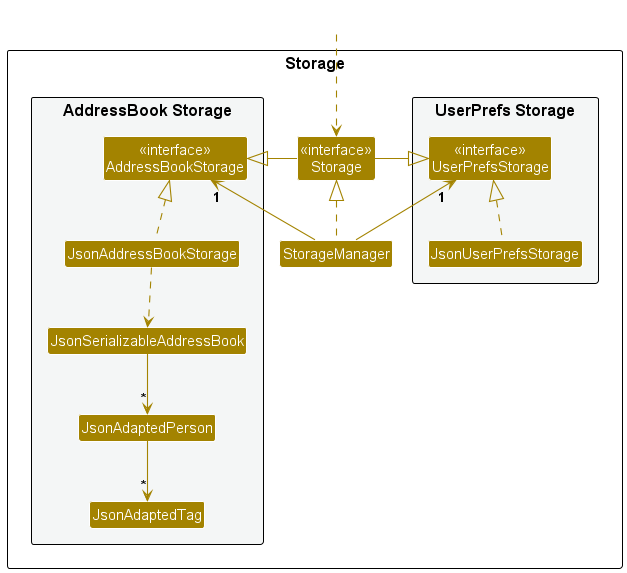
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent’s job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
[Proposed] Undo/redo feature
Proposed Implementation
The proposed undo/redo mechanism is facilitated by VersionedAddressBook. It extends AddressBook with an undo/redo history, stored internally as an addressBookStateList and currentStatePointer. Additionally, it implements the following operations:
-
VersionedAddressBook#commit()— Saves the current address book state in its history. -
VersionedAddressBook#undo()— Restores the previous address book state from its history. -
VersionedAddressBook#redo()— Restores a previously undone address book state from its history.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#commitAddressBook(), Model#undoAddressBook() and Model#redoAddressBook() respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
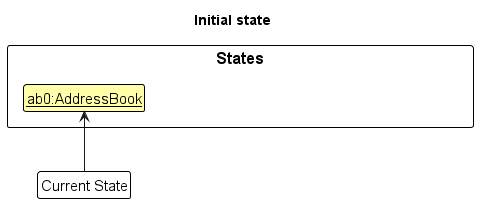
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedAddressBook will be initialized with the initial address book state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single address book state.
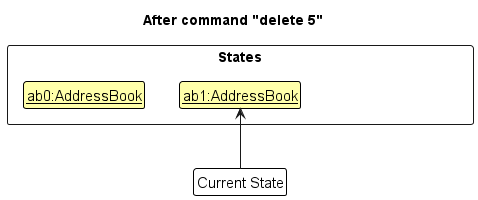
Step 2. The user executes delete 5 command to delete the 5th company in the address book. The delete command calls Model#commitAddressBook(), causing the modified state of the address book after the delete 5 command executes to be saved in the addressBookStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted address book state.
Step 3. The user executes add n/David … to add a new company. The add command also calls Model#commitAddressBook(), causing another modified address book state to be saved into the addressBookStateList.
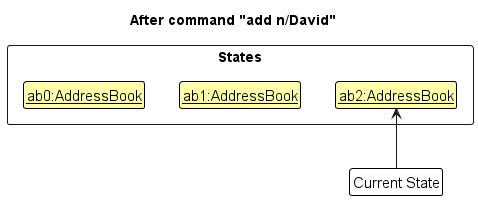
Model#commitAddressBook(), so the address book state will not be saved into the addressBookStateList.
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the company was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the undo command. The undo command will call Model#undoAddressBook(), which will shift the currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous address book state, and restores the address book to that state.
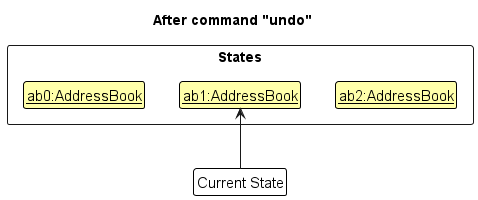
currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial AddressBook state, then there are no previous AddressBook states to restore. The undo command uses Model#canUndoAddressBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather
than attempting to perform the undo.
The following sequence diagram shows how an undo operation goes through the Logic component:
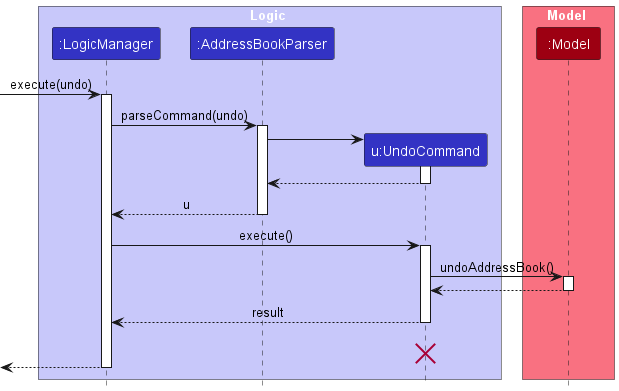
UndoCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Similarly, how an undo operation goes through the Model component is shown below:
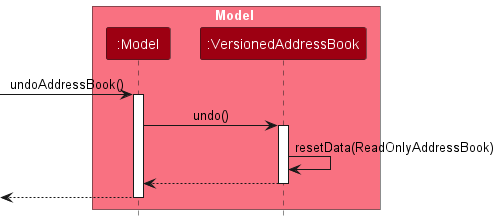
The redo command does the opposite — it calls Model#redoAddressBook(), which shifts the currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the address book to that state.
currentStatePointer is at index addressBookStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest address book state, then there are no undone AddressBook states to restore. The redo command uses Model#canRedoAddressBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the redo.
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command list. Commands that do not modify the address book, such as list, will usually not call Model#commitAddressBook(), Model#undoAddressBook() or Model#redoAddressBook(). Thus, the addressBookStateList remains unchanged.
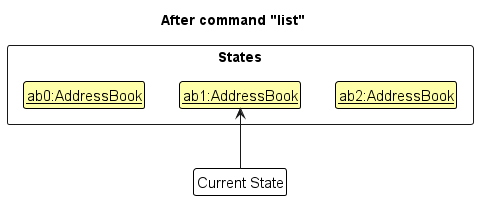
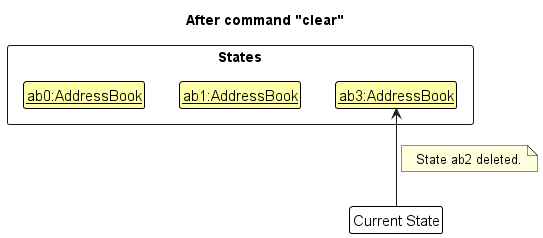
Step 6. The user executes clear, which calls Model#commitAddressBook(). Since the currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the addressBookStateList, all address book states after the currentStatePointer will be purged. Reason: It no longer makes sense to redo the add n/David … command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
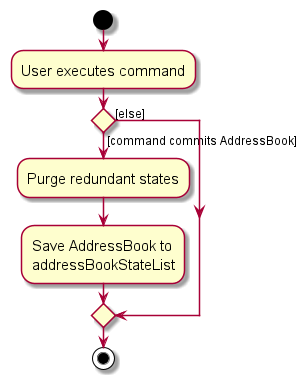
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command:
Design considerations:
Aspect: How undo & redo executes:
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the entire address book.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: May have performance issues in terms of memory usage.
-
Alternative 2: Individual command knows how to undo/redo by
itself.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
delete, just save the company being deleted). - Cons: We must ensure that the implementation of each individual command are correct.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
{more aspects and alternatives to be added}
[Proposed] Data archiving
{Explain here how the data archiving feature will be implemented}
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- Computer Science students mass applying for internships
- Well-accustomed to CLI-interfaces and prefers keyboard shortcuts over GUI interfaces
- Fast typist who prefers typing to mouse interactions
- Tends to be forgetful about deadlines
- Makes occasional data entry mistakes
- Needs to manage a significant number of internship applications simultaneously
- Is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: Helps students keep track of prospective and current internship companies and their application status in a centralized location, with reminders for upcoming application deadlines, interviews, and assessments. Manages applications faster than a typical mouse/GUI driven app.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * |
first-time applicant | track potential companies I might apply for in the future | apply for them after I have made substantial progress |
* * * |
applicant who loves structure and organisation | add my interested companies | store and organize my internship applications |
* * * |
user who dislikes clutter | delete an existing internship application | remove outdated or unnecessary entries from my tracker |
* * |
mass internship applicant | record the OA questions that I have done before | revise them for future interviews |
* * |
overzealous student applying to a ridiculous number of companies | assign scores to each aspect of a company | compare the companies based on my preferences |
* * |
person who holds regard in contacting HR | store HR contact details in the tracker | reach out to them easily |
* * |
student that is able to land multiple internships | sort the companies by pay | renegotiate my salaries and make decisions between offers more easily |
* * |
person who is concerned with work life balance | sort the companies by internship benefits | maximize my work life balance when deciding on an internship |
* * |
busy applicant | sort my internship applications by the stages | keep track of where I am in each process |
* * |
prospective user | differentiate between applications that have referral and those who don’t | prioritize the applications that I want to focus on |
* * |
intern with specific work preferences | sort by the mode of work that I most prefer | prioritize the interns with the type of work arrangement that I prefer |
* * |
person who wants to save time | sort by travel duration | prioritize those that are closer to me |
* * |
applicant applying for different roles | have easy access to different versions of my resume | apply to different role openings quickly without needing to edit my resume regularly |
* * |
user who often forgets deadlines | set reminders for application deadlines | not miss important application deadlines |
* * |
user who often forgets deadlines | set reminders for OA deadlines | not miss important OA deadlines |
* * |
user who often forgets deadlines | set reminders for interview deadlines | never miss important interview deadlines |
* |
user who prefers keyboard shortcuts over mouse clicks | always be typing while minimizing having to switch to my mouse/trackpad | save time and work efficiently |
* |
organised person | filter applications by status (Applied, Interviewing, Offer, Rejected) | focus on pending or priority applications |
* |
forgetful person | see my notes that I took about each company | prepare for my interviews |
* |
busy student with packed schedules | see which internship periods will clash with my school term | take note of them and decide accordingly if I can afford the clash |
* |
busy applicant | track my current open applications that I might have left halfway | get back to my open applications that I have done halfway |
* |
forgetful Computer Science student | sort my internship applications by the next deadline | remember what interview or assessment to prepare for next |
* |
user who makes frequent careless mistakes | update the details of an existing company | keep the information accurate and up-to-date |
* |
user | view all companies at once | see the overall status of my applications |
* |
impatient user | search applications by name, company, role, or application status | quickly locate a specific application without scrolling through the entire list |
* |
student that loves to be organised | sort applications alphabetically or by other fields (dates, ranking) | browse applications more efficiently |
* |
error-prone person | undo or redo my recent changes | correct mistakes easily |
* |
careless student | detect potential duplicate applications | keep my application book clean and not resubmit applications |
* |
user who may not always have all the necessary information ready at once | create a partial entry with whatever details I have at the moment | fill in the rest later when I acquire it |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the Cerebro and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC01 - Delete a company
MSS
- User requests to list companies
- AddressBook shows a list of companies
- User requests to delete a specific company in the list
-
AddressBook deletes the company
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
-
2a1. Cerebro shows a message indicating no companies to delete.
Use case ends.
-
-
3a. The given index is invalid (non-numeric, zero, negative, or out of range).
-
3a1. Cerebro shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
-
3b. The index is missing.
-
3b1. Cerebro shows the correct command format.
Use case ends.
-
-
3c. Multiple indices are provided.
- 3c1. Cerebro carries out deletion of multiple companies.
-
3c2. Cerebro shows success message for the deletion of multiple companies.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC02 - List all companies
MSS
- User requests to view all companies
- Cerebro displays a numbered list of all companies with their application status and key details
-
Cerebro shows the total count of companies
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
- 2a1. Cerebro shows a message indicating no companies have been added yet.
-
2a2. Cerebro suggests using the add command to get started.
Use case ends.
-
1a. Extra parameters are provided with the list command.
- 1a1. Cerebro shows an error message with the correct command format.
Non-Functional Requirements
Performance
- The system shall respond to any page load, search, filter, or sort operation within 3 seconds for up to 100 applications per user.
- Reminder notifications (application deadlines, OA deadlines, interviews) shall be delivered within 1 minute of the scheduled time.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
Reliability & Availability
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java ‘17’ or above installed
- The system shall have 99.5% uptime, ensuring users can access their data at all times.
- Data consistency shall be maintained at all times across features (notes, reminders, rankings, deadlines).
Security & Privacy
- Only authenticated users can access their data; no cross-user data leakage shall occur.
- The system shall comply with applicable data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, PDPA).
Scalability & Capacity
- The system shall support at least 1000 concurrent users without significant degradation of performance.
- Database and infrastructure shall support growth in data volume, e.g., hundreds of applications per user.
- Notification systems shall scale to handle a large number of users simultaneously.
Interoperability
- The system shall support import/export of application data in standard formats (CSV, JSON) for integration with other tools.
Data & Backup
- All user data shall be persisted reliably and backed up daily.
- In the event of system failure, recovery shall be possible within 4 hours.
Usability & Accessibility
- The system shall be usable by first-time users without prior training.
- The interface shall support keyboard shortcuts, CLI-first workflow, and screen reader compatibility. .
Technical/Environment Constraints
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java ‘17’ or above installed
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- CLI-first interface: an interface that prioritises keyboard-only interactions in order to optimise for speed of usage
- Company: Any entity, legally registered or otherwise, that the user can undertake an internship at; a company can have any number of applications
- Application: The entire process of securing a potential internship with the company, starting from the first contact with the company (via email or otherwise) to the point of securing the internship
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
-
{ more test cases … }
Deleting a company
-
Deleting a company while all companies are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list. -
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No company is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
{ more test cases … }
Saving data
-
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- {explain how to simulate a missing/corrupted file, and the expected behavior}
-
{ more test cases … }